DataOps Checklist for Implementing Analytics Data Warehouse
From DevOps to DataOps
It is a lifecycle approach to data analytics, it uses a practical agile approach to orchestrate tools, code, infrastructure to quickly and efficiently deliver high-quality data and improve performance, efficiency and security.
To unblock business operations and uncover insights from messy data silo in among organizations, and adopt advanced data techniques to support business discover and analysis from a variety of data and process.
Here is a checklist of implementations of the DataOps process, especially for data warehouse.
Data Governance and People
Data governance
-
A central location is used to register data sources, most of data data platform is missing this component for registration of data source onboarding: The solution for this is help non-technical users can register their dataset to Data Lake for further processing. The solution for this is a combination of of (1) PowerApp for quickly creating e-forms for datasets metadata registration, (2) LogicApp for customizing the workflow of validation, trigger Data Factory ingestion jobs via API, and (3) Save metadata to MDM.
-
Master Data Management.
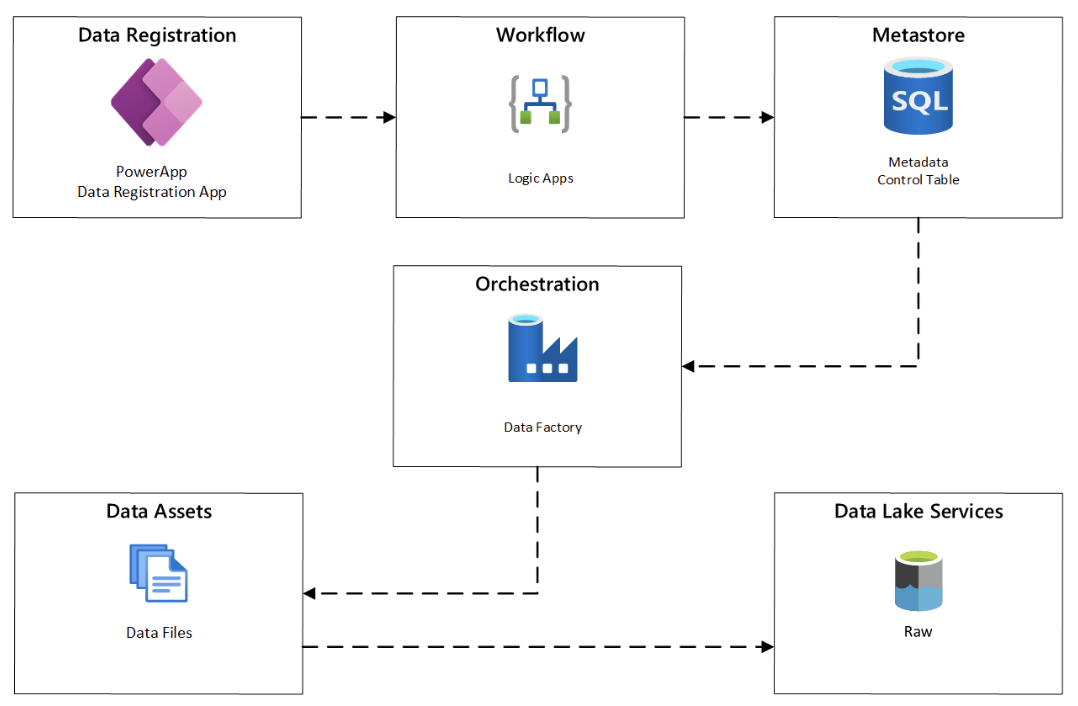
- Data lineage and metadata are available.
- Data is easily discoverable by users, and sensitive data is secured.
- Data and security officers have sightlines into how data is being used, who has access, and where sensitive data might be located.
=> There are several ways to configure and implement the data lineage and metadata management for the platform, with Databricks wer can use the built-in Databricks Workflows, or ADF, or Azure Purview for discover and monitor the lineage and metadata with high efficiency and effective for managing user permissions and secure data using built-in functions.
Example:
-
Databricks: Data Management, Unity Catalog, Sensitive information
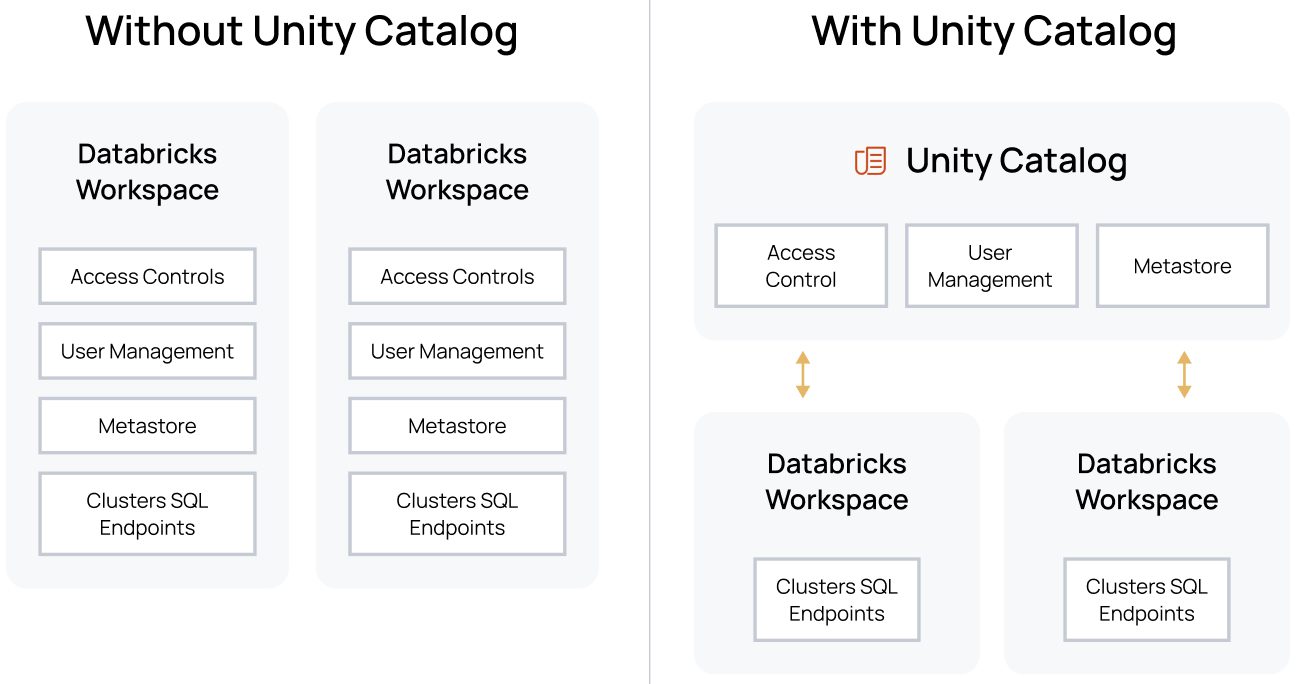
-
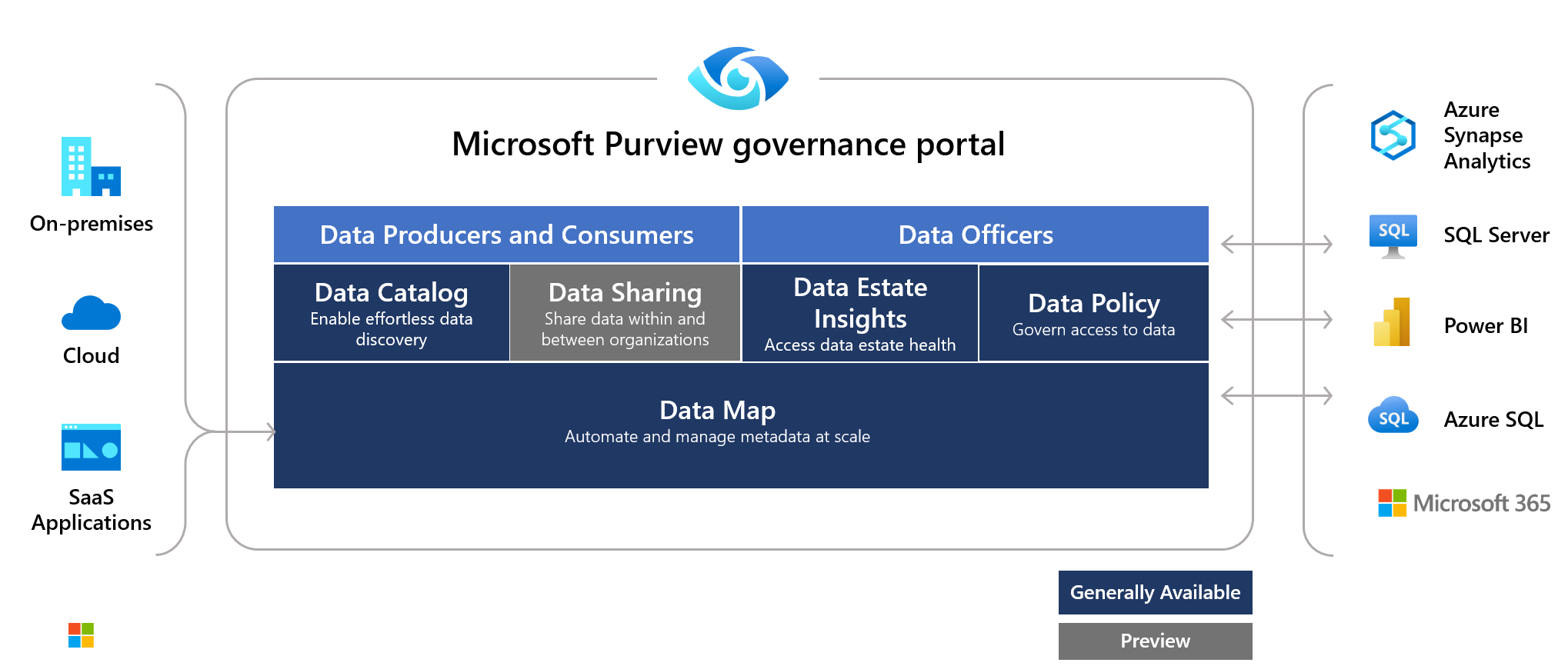
Azure Purview: Data Catalog, Data exploration, Sensitive information
Defined, clear roles
- Engineers, testers, data scientists, operations, data analysts, business users, and data officers all work together and understand their roles in the project.
- Stakeholders are identified, and you understand what’s motivating stakeholders to start making data-driven decisions.
=> Clearly defined within Group and User models in user-group-security group services or integrated with Azure Active Directory with connection helps to leverage the permissions set in On-premises.
=> Best practices is define the suggested permissions set and groups with relevant permissions with least privileges and limitations of the permissions.
=> Those defined user and group can be leveraged with Databricks and Azure Purview for access control and user management.
Use cases for data movement
-
The use cases for streaming, interactive, and batch analytics are resolved. Clearly know the use cases and panpoints of the data movement issues and resolved accordingly, the best approach for data processing even Streaming or Batch is using Apache Spark for processing data the EventHub for streaming data otherwise Data Factory for ingesting batch data.
-
The various types of data for each case are clarified, and metrics are defined to motivate making data-driven decisions. During the process of ingesting data, we might face with different scenarios such as delta copy, snapshot and incremental loading data, or Slowly Changing Dimension, Capture Data Change or Rapid Changing Dimension. Those kind of situations need to be considered and implemented exactly once before consume data for downstream processes.
=> With Data Factory and EventHub that helps to make data-driven decisions, event-driven decisions as well as Spark - Databricks that strongly recommended for processing data.
The modern data processing system is Lambda Architect that helps for making simplify process of batching and streaming data processing.
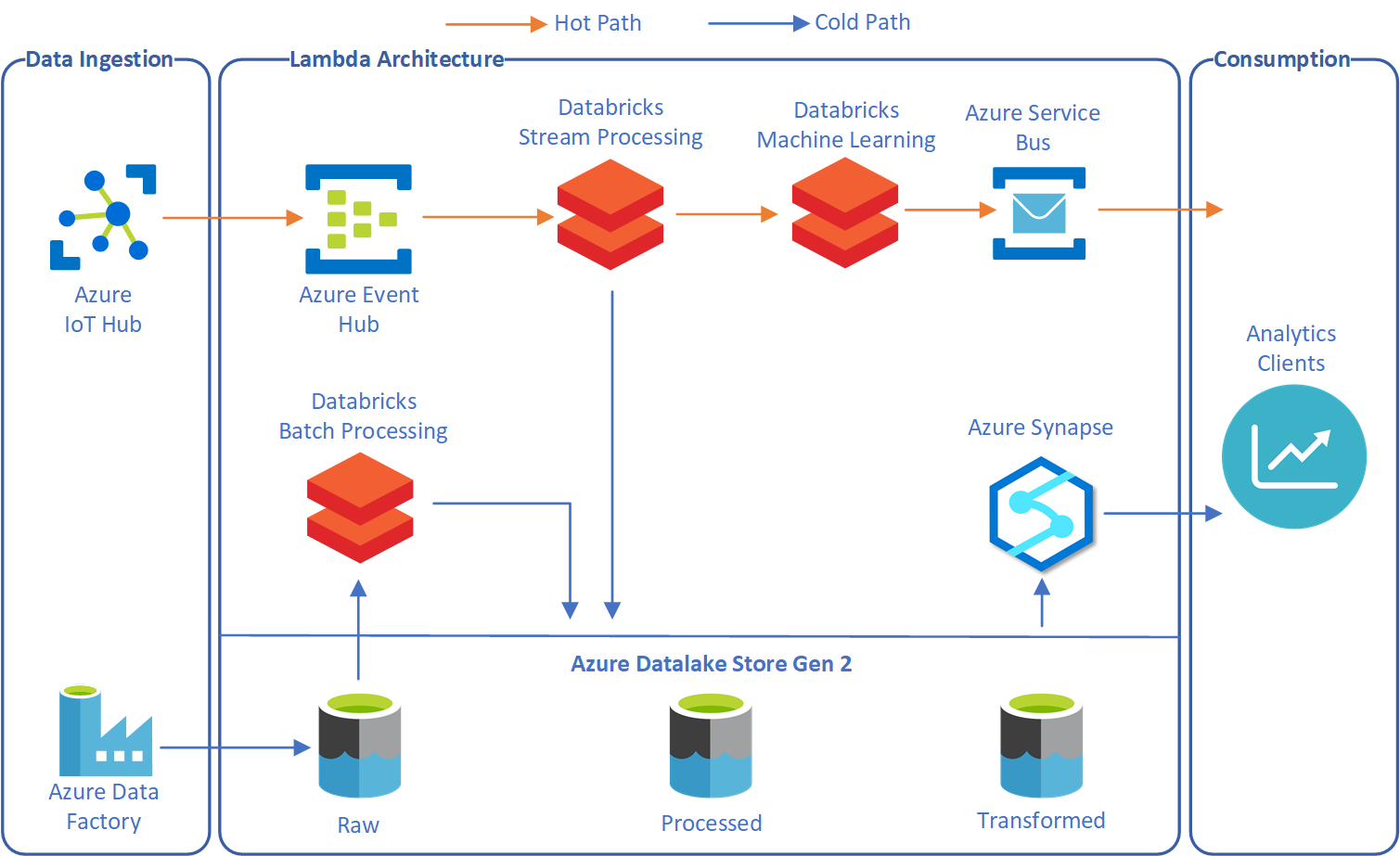
Data tools
- Data tools needed to make data easier to access, share, analyze, and secure are identified or developed. Either Databricks or Azure Purview are available for data sharing and analyze operations.
Security and compliance
- All resources, data in transit, and data at rest have been audited and meet company security standards. By applying security standards and policies to the dataset, you can manage your data movement encryption and decryption of data. Additionally, you can control resources by adding tagging attributes when creating resources with IaC (Terraform with values : “Managed by Terraform”)
- By apply security compliance to ensure resources are properly secured and controlled by the platform team.
- There are some features: data encryption and decryption using Databricks, Hashing, KMS, TLS features are required when design and implement data pipelines.
- Network security compliance, Virus scanning is strongly encouraged when auditing data pipelines.
Development
Pipeline design patterns
-
Data pipelines are designed for reuse and use parameterization. Using common design patterns for design jobs. For example: template design, metadata programmatic design,… Using Core Functional design and replaceable components design that helps the data applications can be extendable and easy of use.
-
Pipelines solve common ETL problems. By apply Data Validation and Data Quality Gate checking, with some KPIs and metrics to ensure the data is qualified before merging to next data layer. Ex: No duplicated, be able to backfilling, re-processing, early detected errors,…
Using Notebooks template and orchestrate using ADF/Databricks workflows to help to quickly deploy a data pipeline.
Centralized ingestion
-
A centralized platform hosts pipelines for all external and internal data sources. This allows for simplified management, monitoring, security, and standardization of data movement. Using data governance and data lineage data service like Azure Purview, Azure helps us to manage internal and external data sources with monitoring features and user management control features.
-
Costs associated with handling data are also centralized. Central control can help minimize cost and maximize efficiency.
Centralized computations
- A central team defines metrics and determines how to compute those metrics. This allows for consistency across the organization and limits confusion about where to make updates to computations. It also creates one source for metrics definitions, governance, testing, and quality controls.
- Auditing and logging features are always enabled for data platforms or any kind of systems that support to monitor and optimize system using pre-defined metrics. Azure Monitor is well-formed for monitoring services in Azure.
- Also the custom metrics definition is highly recommended for optimization purposes.
Data abstraction
- Reporting uses a data abstraction layer. This allows the use of consistent business terminology, a simplified view of data, and minimal effect on data consumers when new versions of the data are made available.
- Meaning of data is determined by the data onboarding and data exploration processes. By details of the data provided by data owners and data stewards, data catalog is a tool to provide data dictionary.
Source control
- Data-related infrastructure, database schemas and procedures, ETL processes, and reports are treated as code and managed in a repository.
- All changes are deployed and tested via a Development, Testing, Acceptance, and Production (DTAP) stack.
- Azure DevOps supports for DTAP process that helps to enable data service applications as IaC and manged as version. Example: CICD pipelines
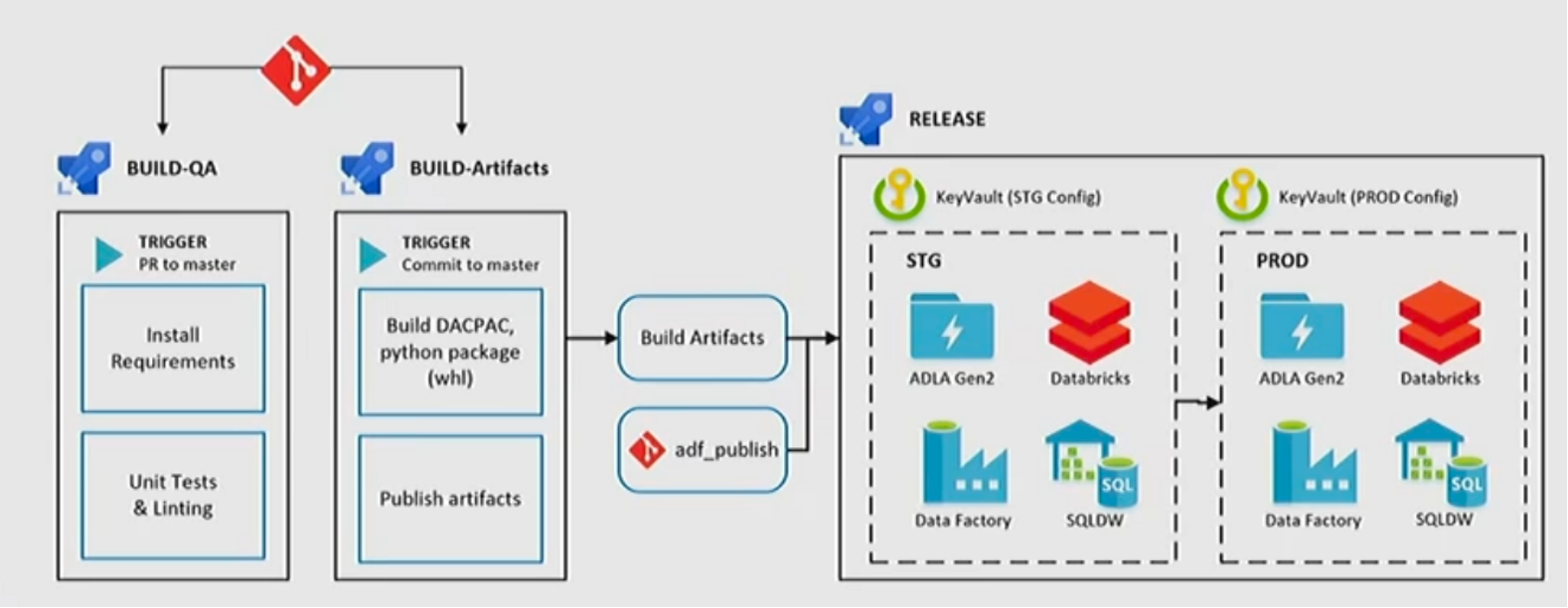
Testing and release
DTAP environments
- Non-production environments that mimic the production environment are available.
- Builds and deployments are run and tested on the non-production environment before a production push.
- Developers can deliver reproducible results in all environments.
=> Using ADO with Azure Pipelines Build/Release to deploy version of code to target environment
Testing
- Unit, end-to-end, and regression tests run at a specified frequency and interval. All tests are in source control and run as part of a build and deploy process. Post-deployment end-user input is welcome and incorporated into testing as appropriate.
=> Using ADO with Azure Build to Validate and Trigger Test Pipeline with Parameter which are required inputs of Databricks Notebook/Job for validating data.
Build and deploy process
- A gated process deploys changes to the production environment.
- Changes are tested in the development and test environments. Changes are certified before they go to production. This process is as automated as possible.
Monitoring
Alerting and remediation
- Operations is alerted to any errors. You can respond to feedback quickly and have a process for quickly addressing issues as they arise.
- Pipelines are observable.
- By apply logging standards with audit logging tables and monitoring services, you can keep track of performance or abnormalities within pipelines or data assets.
- By defining logging levels per seniority and priority levels, you can monitor SLA and aware issues as they occur and resolve them appropriately as soon as possible.
Efficiency
- Data movement is efficient. Some of problems when data movement with inconsistent data volumes are required the processing engine needs to be scalable.
- Infrastructure can be scaled to meet volume and velocity needs. Serverless is well-supported scalability and high availability but there are many other considerations when decided to choose the serverless architecture.
- Data is reusable whenever possible. Keep data in backup and data retention is encouraged for making data always available available for analysis. Azure Blob Storage supports Hot and Cold methods for storing data.
Statistical process control (SPC)
- SPC is used to monitor and control the data pipelines. The metrics associated with the process of data pipelines are calculated by SLA, % passed/failed, performances, processing rate, time execution,…
- You can use the outputs of pipelines to determine the next step in the data flow as the even-driven architect, it will be used to input to other workflow like alerting or notification. Azure LogicApp is best suited for this purpose.
Conclusions
- For defining constraints and specifications of DataOps process, that helps to gain pretty much benefits from data platforms.
- Sample implementation and architecture are available within Azure Cloud Data Services, there are several different implementations and architecture and customized by use-cases.
- The architect is alternatively changed by other services with critical consideration.
Notes: Referenced in the documentation: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/checklist/data-ops