Getting Started with DataOps
-
DataOps is a set of practices, processes and technologies that combines an integrated and process-oriented perspective on data.
-
Automation and methods from agile software engineering to improve quality, speed, and collaboration and especially to promote a culture of continuous improvement in the area of data analytics.
-
Leverage the Data Quality Dimensions: Completeness, Accuracy, Consistency, Uniqueness, Timeliness, Validity. The Entities (Table, Dataset, Columns, Rows) are being to verify with expected results.
Principle Design of DataOps
- Making sure data is properly verified
- Applying Agile Processing (DevOps)
- Testing with data event driven
- Building with Micro-services patterns
- Supporting Scaling
Architecture Design
This is service design
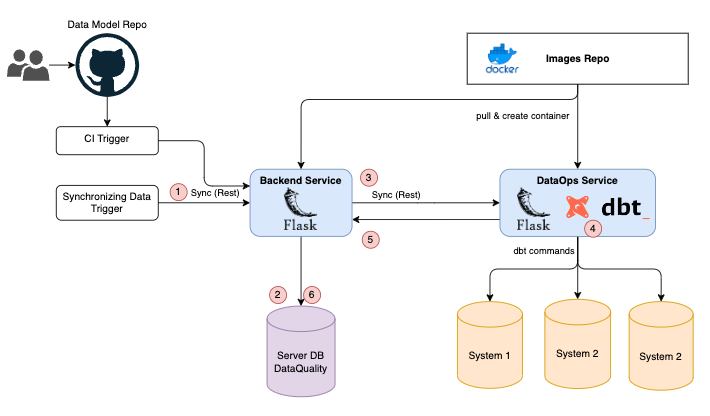
Leverage Micro-services, data flows of data ops processing will be explained in the following:
- Trigger will send a message request to Backend Service
- Tracking message request and get configuration
- Send request to DataOps Service, DataOps is an containers pod with Custom Images which has registered on Images repo
- Running
dbtcommand on target database - Send results and acknowledge message to Backend Service, result will be stored in StringX internal database
How StringX will being used in data quality check gates?
By performing quality check on the table defined in the configuration table, we can determine which engineering rules and/or business rules will be applied to the table.
There two three different set of configurations:
- Right Perform Data Quality Check
- Trigger external DataOps Service for async operation quality checks
You can monitor the quality, data models using dbt (see in the capture)
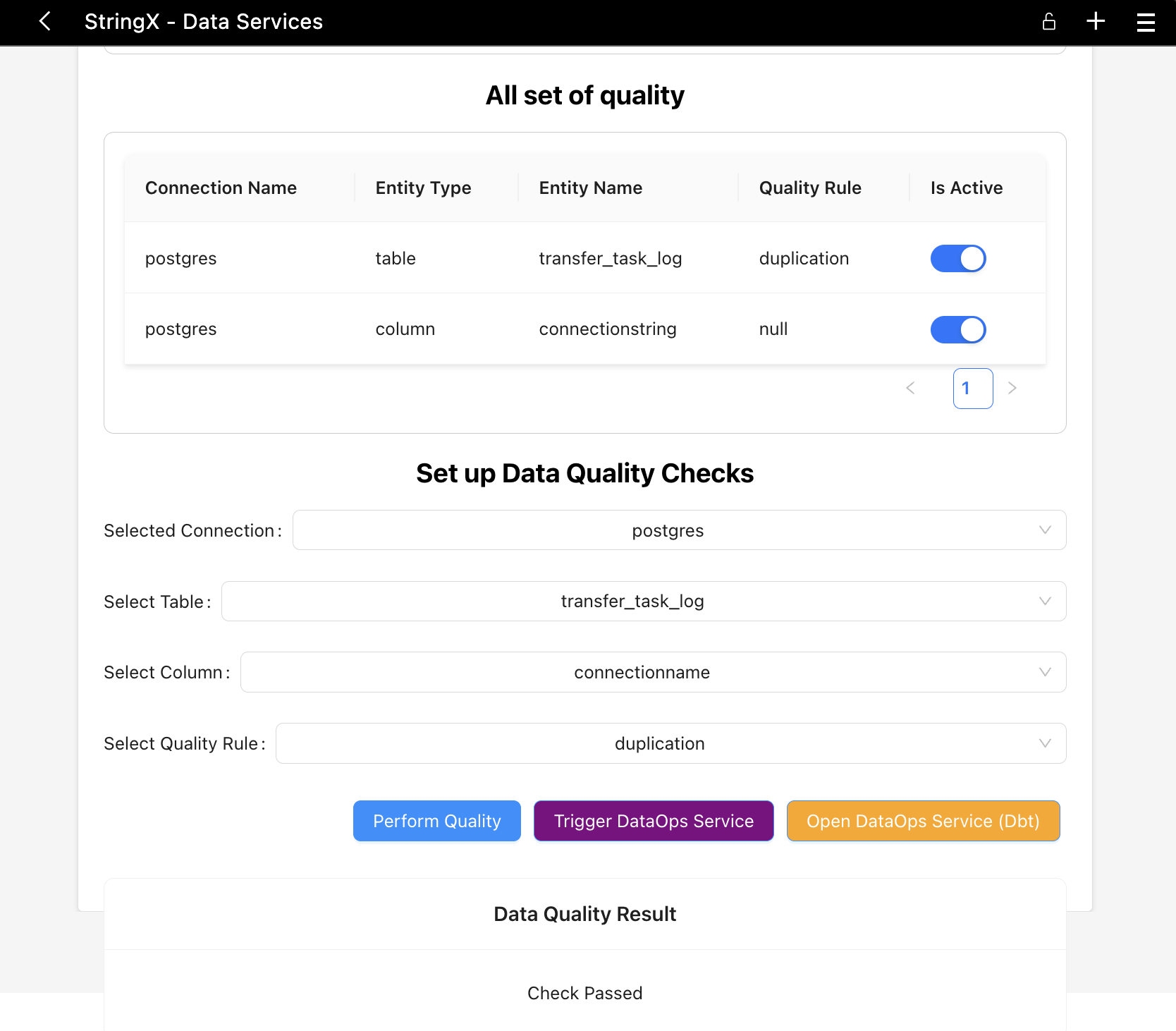
Setup on Local Machine
By self-creating the application and running quality tests with StringX Application.
Creating container services for Data Operation with sample structure of Docker Image.
# Stage 1: Build the dbt container
FROM ghcr.io/dbt-labs/dbt-postgres AS dbt-builder
# Add any additional dependencies needed for dbt here
COPY stringx /usr/app/dbt
WORKDIR /usr/app/dbt
# Build dbt
# RUN dbt deps
# RUN dbt seed
# RUN dbt run
# Stage 2: Build the Flask API container
FROM python:3.8 AS api-builder
# Add any additional dependencies needed for your Flask API here
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY api /usr/app/api
WORKDIR /usr/app/api
ENV DBT_PROFILES_DIR=/usr/app/dbt/
ENV DBT_PROJECT_DIR=/usr/app/dbt/
EXPOSE 5001
EXPOSE 8001
# Stage 3: Create the final image by combining dbt and Flask API
FROM api-builder AS final-image
COPY --from=dbt-builder /usr/app/dbt /usr/app/dbt
WORKDIR /usr/app/api
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
# docker build . -t dbt-data-ops:latest --no-cache
# docker run -p 127.0.0.1:5001:5001 --name dbt-dataops-service dbt-data-ops:latest
Create container and start service using below script
echo "start to create a container"
docker ps
echo "clear up container"
docker stop dbt-dataops-service
docker rm -f dbt-dataops-service
docker build . -t dbt-data-ops:latest --no-cache
echo "start to create container"
docker run -p 127.0.0.1:5001:5001 -p 127.0.0.1:8001:8001 --name dbt-dataops-service dbt-data-ops:latest
echo "verify docker container"
docker ps
Using Postman to test API with sample payloads
Notes: Run dbt docs generate/serve to generate docs and dbt portal.
Folder Structure
.
├── Dockerfile
├── README.md
├── api
├── app.py
├── requirements.txt
├── sending_kafka_messages.py
├── start-service.sh
└── stringx